As renewables are making a fast and determined entry in most countries’ electricity mix, the need to provide ample and secure base load is becoming a priority. With coal and lignite fired plants being gradually retired as the region tries to decarbonise and transit to clean fuels, the burden for base load provision has fallen on natural gas. However, gas supply has become subservient to regional geopolitics since the start of the war in Ukraine while prices are maintained at high levels, trading two to three up to what they were before the energy crisis of 2022.
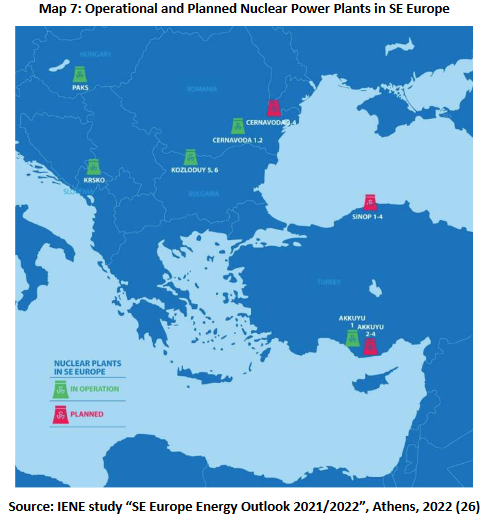
As IENE’s latest Research Note (here) points out nuclear power already plays a crucial role in providing stable, low -carbon base load electricity, but only few countries in SE Europe currently rely on it significantly. In SE Europe there are countries- Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania, Slovenia and Croatia- that currently operate nuclear power plants (NPP’s). To these we should add Hungary, which has some 1.9 GW of installed nuclear power at the Paks complex. Although strictly not part of South East Europe, Hungary plays an important role as an electricity conduit for the whole region because of its extensive infrastructure and critical location. While Turkiye, which is expected to build no fewer than 3 NPP’s over the next decade, is due to commission its first 1.2 GW ( out of four) NPP at Akkuyu before the end of this year.
Over the last 15 years, IENE has closely monitored developments in the region’s nuclear power sector. In this context, the Institute has successfully organised two regional conferences. Under the general title “The Nuclear Option for SE Europe: A Critical Appraisal”, the first such conference was convened in Sofia on May 19, 2009, and the second one in Bucharest on May 6,2015. Further monitoring of the nuclear power situation in the region was made by IENE thorough its various reports and most notably through its flagship publication, the SEE Energy Outlook (2011, 2017, 2022)
In its forthcoming “Outlook” report, to be released in October this year, a special chapter authored by nuclear expert Dr. Aliki van Heek is contributed. In this chapter a thorough analysis of the current nuclear power situation is made while the technical and non -technical obstacles for greater nuclear power utilisation are discussed.
Also, the outlook for higher nuclear power penetration in SEE’ electricity mix is examined, including progress achieved in adopting SMR technology. In this context the investment and production cost considerations are also being investigated.